Picture by Erika Wittlieb by way of Pixabay.com
Business actual property lending continued to gradual within the first quarter, within the face of banking system stress and volatility within the monetary markets, in accordance with a brand new report from CBRE.
CBRE’s Lending Momentum Index, which tracks CBRE-originated business mortgage closings within the U.S., declined by 33 % from the fourth quarter of 2022—and by 53.5 % versus the sturdy mortgage quantity of 12 months prior. The index closed the primary quarter at 204.
The Federal Reserve’s dedication to scale back inflation with aggressive charge hikes continued to intensify market uncertainty via the primary quarter, in accordance with Rachel Vinson, president of Debt & Structured Finance, U.S. for Capital Markets at CBRE. She commented in ready remarks that loads of debt capital stays obtainable, however elevated borrowing prices coupled with credit score tightening continues to place downward stress on lending exercise. Debtors will proceed to go for shorter-term, fixed-rate debt with shortened name safety till volatility begins to normalize, Vinson concluded.
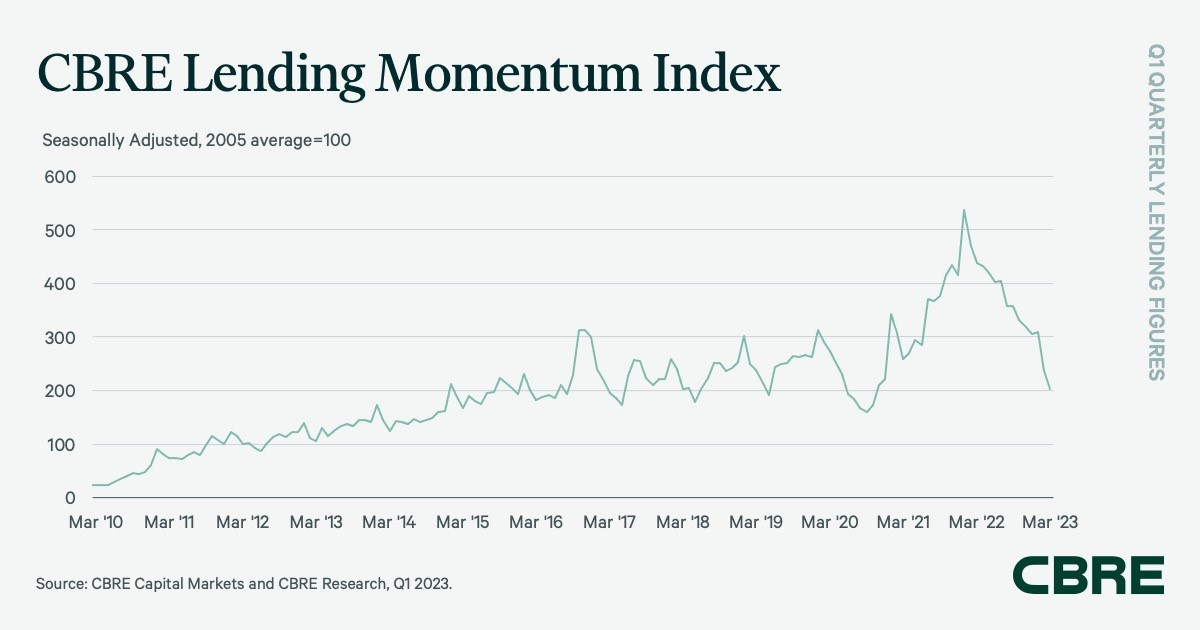
CBRE Lending Momentum Index Q1 2023. Chart courtesy of CBRE
Current much-publicized financial institution failures however, banks have been the dominant gamers, with 41.1 % of CBRE’s non-agency mortgage closings for the fourth consecutive quarter, although this was down from 58 % within the fourth quarter. CBRE famous that this end result “was pushed by a various set of smaller native and regional banks, in addition to credit score unions.”
About one-third of financial institution loans have been for building initiatives, totally on the multifamily facet, whereas the remainder have been cut up between acquisition loans and refinancings.
READ ALSO: Workplace House owners Face Financing Dilemma
Life firms have been the following most energetic lenders within the first quarter, with 23 % of closed non-agency loans, which was simply above their fourth-quarter share. Mortgage closings within the first quarter included a excessive proportion of five-year offers, with a mean 52 % loan-to-value ratio, CBRE reported.
Debt funds, mortgage REITs and different various lenders accounted for 20.2 % of mortgage closings within the first quarter, corresponding to their fourth-quarter portion.
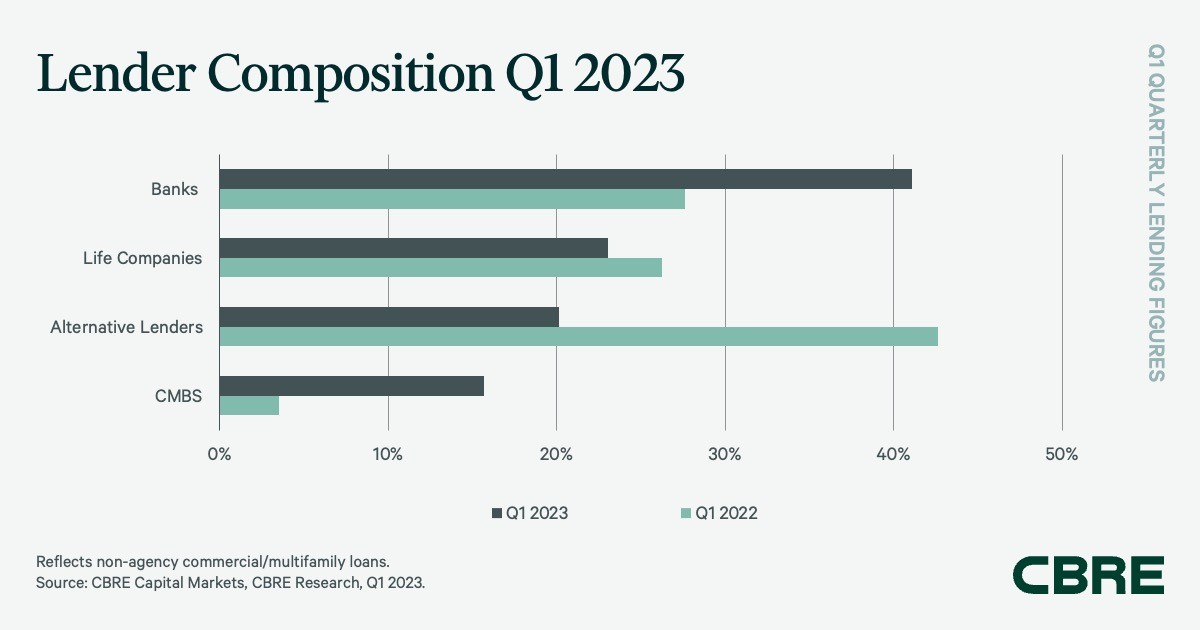
Lender Composition Q1 2023. Chart courtesy of CBRE
“Increased spreads and rate of interest cap prices created a difficult setting for financing floating-rate bridge loans,” CBRE mentioned.
Securitization, charges, phrases
Collateralized mortgage obligation issuance within the first quarter consisted of two offers totaling simply $1.1 billion, versus a complete of $15.2 billion 12 months earlier.
CMBS conduit loans accounted for 15.7 % of non-agency mortgage quantity within the first quarter, which was up from 2 % within the earlier quarter. Industrywide CMBS origination quantity was solely $5.9 billion within the first quarter, a significant fall from the $29.1 billion within the first quarter of 2022.
“Increased mortgage charges and mortgage constants have been a key function of mortgage underwriting standards” within the first quarter, with common mortgage charges rising by 38 foundation factors quarter-over-quarter, CBRE reported.
Nevertheless, mortgage constants rose by solely 13 foundation factors, to 77.6 %, pushed by a rise within the share of loans that carried partial or full interest-only phrases, the report famous.
Lastly, underwritten debt yields and cap charges on closed loans climbed by 29 foundation factors from the earlier quarter to a mean of 5.61 %, CBRE acknowledged.










